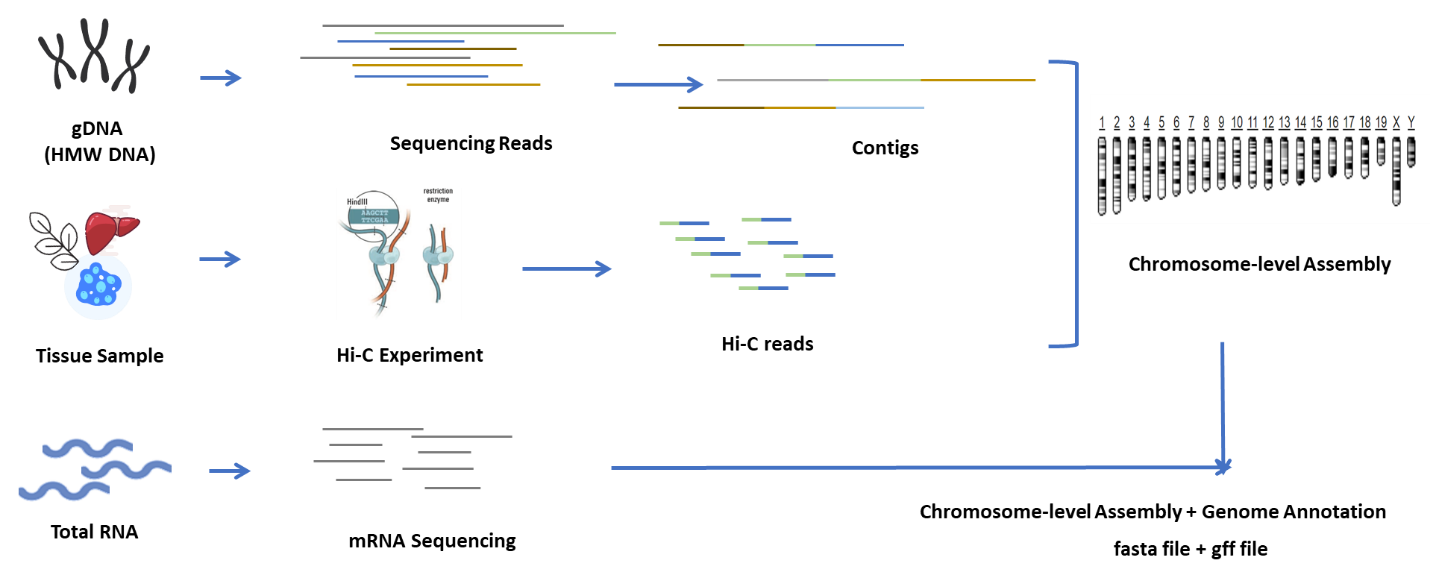
Plant/Animal De Novo Genome Sequencing
Service Features
● Integration of multiple sequencing and bioinformatic services in a one-stop solution:
Genome survey with Illumina to estimate genome size and guide subsequent steps;
Long read sequencing for de novo assembly of contigs;
Hi-C sequencing for chromosome anchoring;
mRNA sequencing for annotation of genes;
Validation of the assembly.
● Service suitable for the constructing novel genomes or improvement of existing reference genomes for species of interest.
Service Advantages

Development of sequencing platforms and bioinformatics in de novo genome assembly
(Amarasinghe S L et al., Genome Biology, 2020)
● Extensive Expertise and Publication Record: BMKGene has accumulated massive experience in high-quality genome assembly of diverse species, including diploid genomes and highly complex genomes of polyploid and allopolyploid species. Since 2018, we have contributed to over 200 high-impact publications, and 15 of them are published in Nature Genetics.
● One-stop Solution: our integrated approach combines multiple sequencing technologies and bioinformatic analyses into a cohesive workflow, delivering a high-quality assembled genome.
● Tailored to Your Needs: Our service workflow is customizable, allowing adaptation for genomes with diverse features and specific research needs. This includes accommodating giant genomes, polyploid genomes, highly heterozygous genomes, and more.
● Highly Skilled Bioinformatics and Laboratorial Team: with great experience in both the experimental and bioinformatics front of complex genome assemblies and a series of patents and software copyrights.
● Post-Sales Support: Our commitment extends beyond project completion with a 3-month after-sale service period. During this time, we offer project follow-up, troubleshooting assistance, and Q&A sessions to address any queries related to the results.
Service Specifications
|
Genome survey |
Genome assembly |
Chromosome-level |
Genome Annotation |
|
50X Illumina NovaSeq PE150
|
30X PacBio CCS HiFi reads Or 100X Nanopore + 50X Illumina PE150 Or 100X PacBio CLR+ 50X Illumina PE150 |
100X Hi-C |
Illumina PE150 (10 Gb) + (optional) PacBio (40 Gb) or Nanopore(12 Gb) |
Service requirements
For Genome Survey, Genome assembly and Hi-C assembly:
|
Tissue or extracted nucleic acids |
Genome Survey |
Genome Assembly with PacBio |
Hi-C Assembly |
|
Animal Viscera |
0.5-1 g |
≥ 3.5 g |
≥2 g |
|
Animal Muscle |
≥ 5 g |
||
|
Mammalian Blood |
≥ 5 mL |
≥2 mL |
|
|
Poultry/Fish Blood |
≥ 0.5 mL |
||
|
Plant- Fresh Leaf |
1-2 g |
≥ 5 g |
≥ 4 g |
|
Plant -Petal/Stem |
≥ 10 g |
- |
|
|
Plant - Root/Seed |
≥ 20 g |
- |
|
|
Cultured Cells |
|
≥ 1x108 |
≥ 1x107 |
|
Extracted DNA |
Concentration: ≥1 ng/ µL Amount: 30 ng Limited or no degradation or contamination |
Concentration: ≥ 50 ng/ µL Amount: 10 µg/flow cell OD260/280=1.7-2.2 OD260/230=0.8-2.5 Limited or no degradation or contamination |
-
|
For Genome annotation with transcriptomics:
|
Tissue or extracted nucleic acids |
Illumina Transcriptome |
PacBio Transcriptome |
Nanopore Transcriptome |
|
Plant- Root/Stem/Petal |
450 mg |
600 mg |
|
|
Plant – Leaf/Seed |
300 mg |
300 mg |
|
|
Plant - Fruit |
1.2 g |
1.2 g |
|
|
Animal Heart/Intestine |
300 mg |
300 mg |
|
|
Animal Viscera/Brain |
240 mg |
240 mg |
|
|
Animal Muscle |
450 mg |
450 mg |
|
|
Animal Bones/Hair/Skin |
1 g |
1 g |
|
|
Arthropod - Insect |
6 |
6 |
|
|
Arthropod -Crustacea |
300 mg |
300 mg |
|
|
Whole blood |
1 tube |
1 tube |
|
|
Extracted RNA |
Concentration: ≥ 20 ng/ µL Amount: 0.5 µg OD260/280=1.7-2.5 OD260/230=0.5-2.5 RIN ≥ 6 5≥28S/18S≥1 |
Concentration: ≥ 100 ng/ µL Amount: 0.75 µg OD260/280=1.7-2.5 OD260/230=0.5-2.5 RIN ≥ 8 5≥28S/18S≥1 |
Concentration: ≥ 100 ng/ µL Amount: 0.6 µg OD260/280=1.7-2.5 OD260/230=0.5-2.5 RIN ≥ 7.5 5≥28S/18S≥1 |
Recommended Sample Delivery
Container: 2 ml centrifuge tube (Tin foil is not recommended)
(For most of the samples, we recommend not to preserve in ethanol.)
Sample labeling: Samples must to be clearly labeled and identical to the submitted sample information form.
Shipment:
Dry-ice: Samples need to be packed in bags first and buried in dry-ice.
Work flow

Service Work Flow

Experiment design

Sample delivery

DNA extraction

Library construction

Sequencing

Data analysis

After-sale services
Complete bioinformatic analysis, separated in 4 steps:
1) Genome survey, based on k-mer analysis with NGS reads:
Estimation of genome size
Estimation of heterozygosity
Estimate of repetitive regions
2) Genome Assembly with PacBio HiFi:
De novo assembly
Assembly assessment: including BUSCO analysis for genome completeness and mapping back of NGS and PacBio HiFi reads
3) Hi-C assembly:
Hi-C library QC: estimation of valid Hi-C interactions
Hi-C assembly: clustering of contigs in groups, followed by contig ordering within each group and assigning contig orientation
Hi-C evaluation
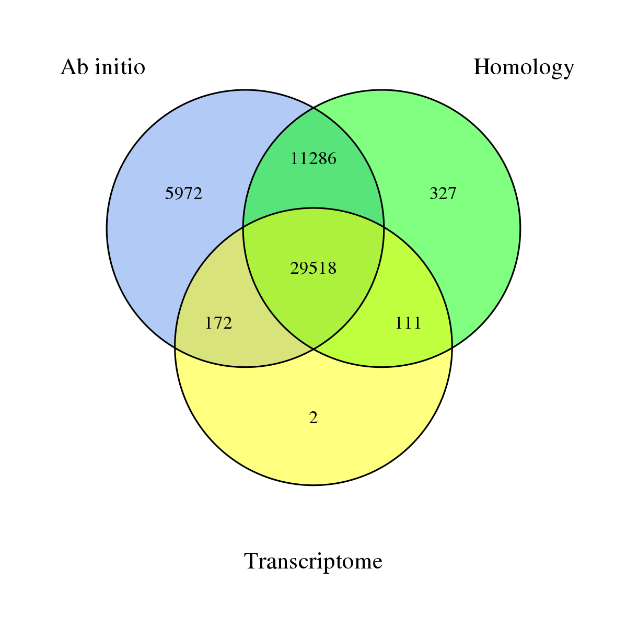
4) Genome annotation:
Non-coding RNA prediction
Repetitive sequences identification (transposons and tandem repeats)
Gene prediction
§ De novo: ab initio algorithms
§ Based on homology
§ Based on transcriptome, with long and short reads: reads are de novo assembled or mapped to the draft genome
§ Annotation of predicted genes with multiple databases
1) Genome Survey- k-mer analysis
2) Genome Assembly
2) Genome Assembly – PacBio HiFi reads mapping to draft assembly
2) Hi-C Assembly – estimation of Hi-C valid interaction pairs
3) Hi-C Post-assembly evaluation
4) Genome Annotation – integration of predicted genes
4) Genome annotation – predicted genes annotation
Explore the advancements facilitated by BMKGene’s de novo genome assembly services through a curated collection of publications:
Li, C. et al. (2021) ‘Genome sequences reveal global dispersal routes and suggest convergent genetic adaptations in seahorse evolution’, Nature Communications, 12(1). doi: 10.1038/S41467-021-21379-X.
Li, Y. et al. (2023) ‘Large-Scale Chromosomal Changes Lead to Genome-Level Expression Alterations, Environmental Adaptation, and Speciation in the Gayal (Bos frontalis)’, Molecular Biology and Evolution, 40(1). doi: 10.1093/MOLBEV/MSAD006.
Tian, T. et al. (2023) ‘Genome assembly and genetic dissection of a prominent drought-resistant maize germplasm’, Nature Genetics 2023 55:3, 55(3), pp. 496–506. doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01297-y.
Zhang, F. et al. (2023) ‘Revealing evolution of tropane alkaloid biosynthesis by analyzing two genomes in the Solanaceae family’, Nature Communications 2023 14:1, 14(1), pp. 1–18. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37133-4.
Challenging case-studies:
Telomere-to-telomere assembly: Fu, A. et al. (2023) ‘Telomere-to-telomere genome assembly of bitter melon (Momordica charantia L. var. abbreviata Ser.) reveals fruit development, composition and ripening genetic characteristics’, Horticulture Research, 10(1). doi: 10.1093/HR/UHAC228.
Haplotype assembly: Hu, W. et al. (2021) ‘Allele-defined genome reveals biallelic differentiation during cassava evolution’, Molecular Plant, 14(6), pp. 851–854. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.04.009.
Giant genome assembly: Yuan, J. et al. (2022) ‘Genomic basis of the giga-chromosomes and giga-genome of tree peony Paeonia ostii’, Nature Communications 2022 13:1, 13(1), pp. 1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35063-1.
Polyploid genome assembly: Zhang, Q. et al. (2022) ‘Genomic insights into the recent chromosome reduction of autopolyploid sugarcane Saccharum spontaneum’, Nature Genetics 2022 54:6, 54(6), pp. 885–896. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01084-1.