
mRNA-seq (NGS) with reference genome
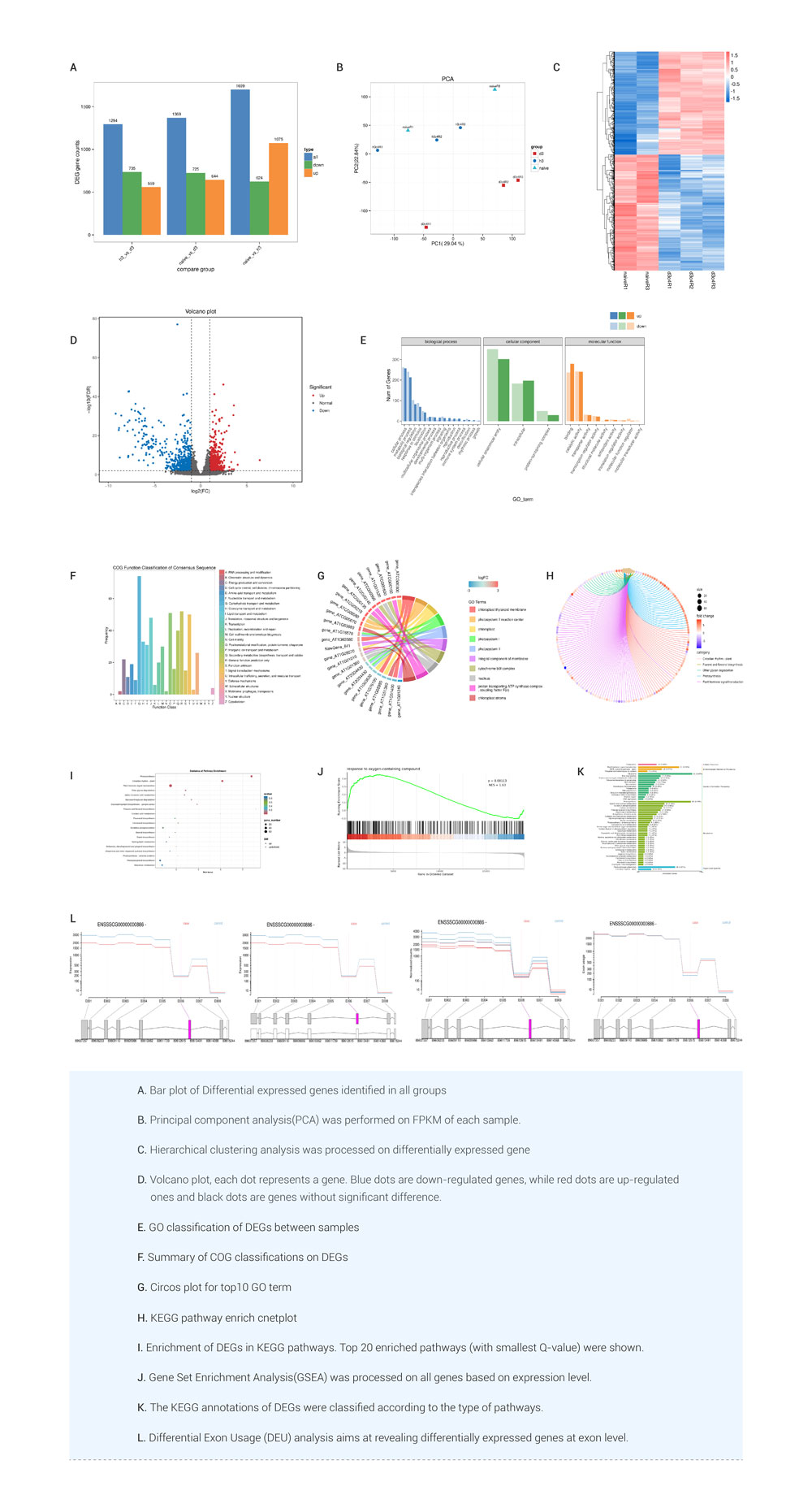
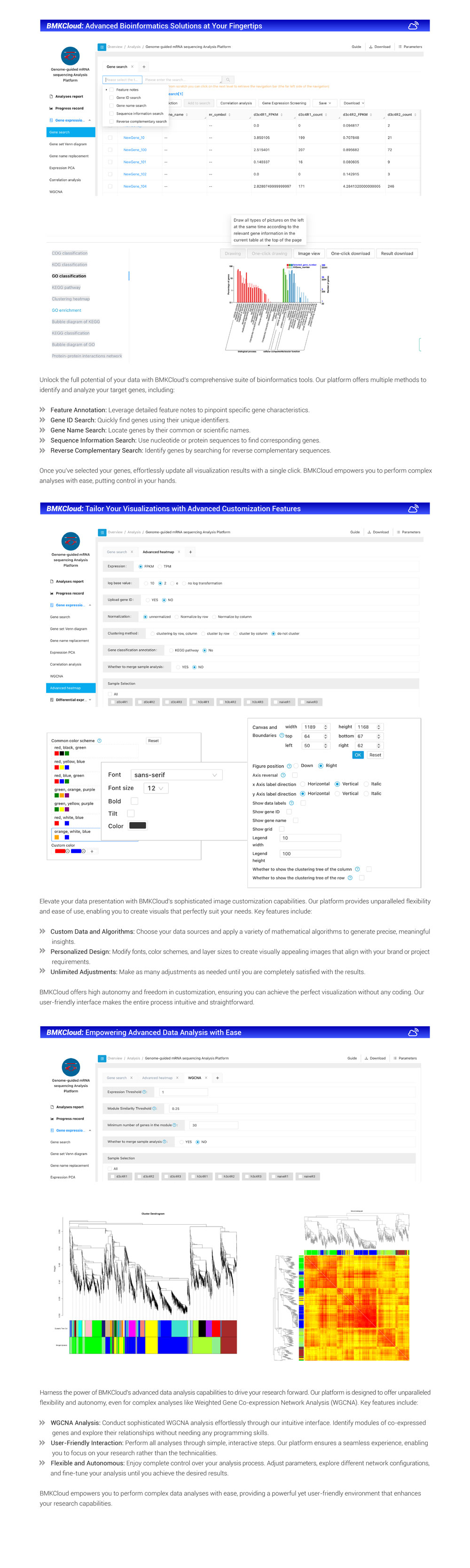
RNA-seq is a standard tool across life and crop sciences, bridging the gap between genomes and proteomes. Its strength lies in discovering new transcripts and quantifying their expression in one assay. It's widely used for comparative transcriptomic studies, shedding light on genes related to various traits or phenotypes, like comparing mutants to wild-types or revealing gene expression under specific conditions. BMKCloud mRNA(Reference) APP integrates expression quantification, differential expression analysis(DEG), and sequence structure analyses into the mRNA-seq(NGS) bioinformatics pipeline and amalgamates the strengths of similar software, ensuring convenience and user-friendliness. Users can upload their RNA-seq data to the cloud, where the App offers a comprehensive, one-stop bioinformatic analysis solution. Additionally, it prioritizes customer experience, offering personalized operations tailored to users' specific needs. Users can set parameters and submit the pipeline mission by themselves, check the interactive report, view data/diagrams and complete data mining, such as: target gene selection, functional clustering, diagramming, etc.
Platform: Illumina, MGI
Strategy: RNA-Seq
Layout: Paried, clean-data.
Library type: fr-unstranded, fr-firststrand or fr-secondstrand
Read length: 150 bp
File type: *.fastq, *.fq, *.fastq.gz or *.fq.gz. The system will automatically pair the .fastq files according to thier file names, e.g. *_1.fastq paired with *._2.fastq.
Number of samples: There are no restrictions on the number of samples, but the analysis time will increase as the number of samples grows.
Recommended Data Amount: 6G per sample

