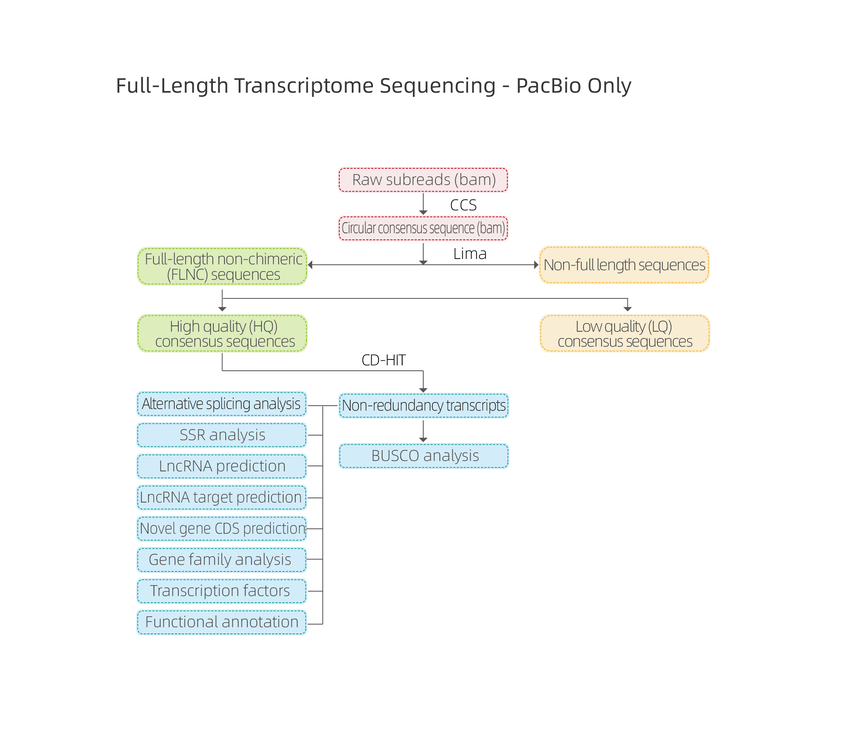
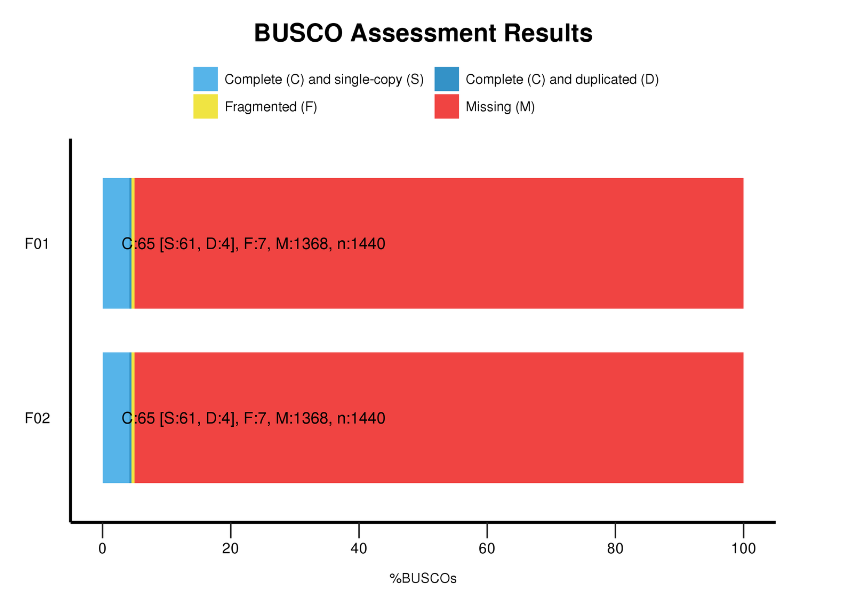
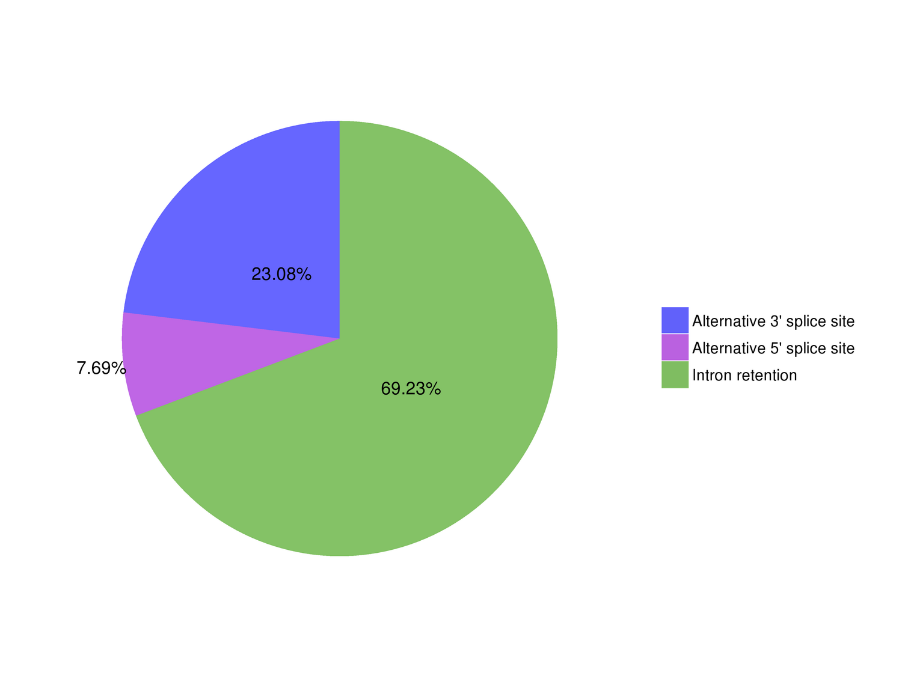
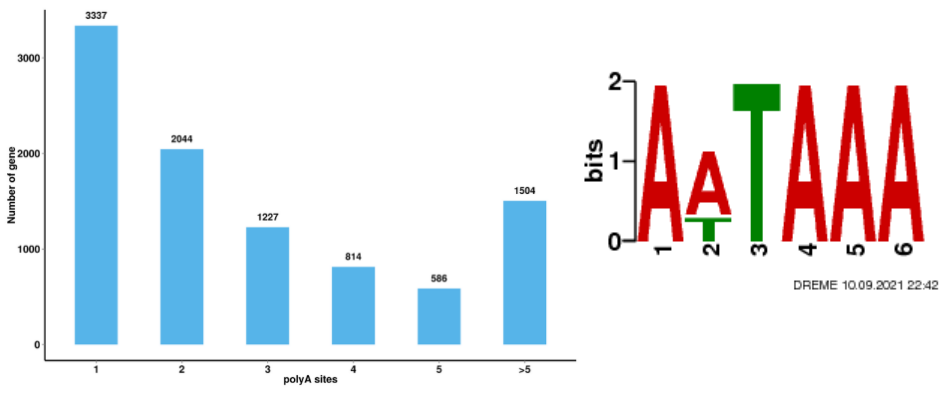
Full-length mRNA sequencing -PacBio
Features
● cDNA synthesis from poly-A mRNA followed by library preparation
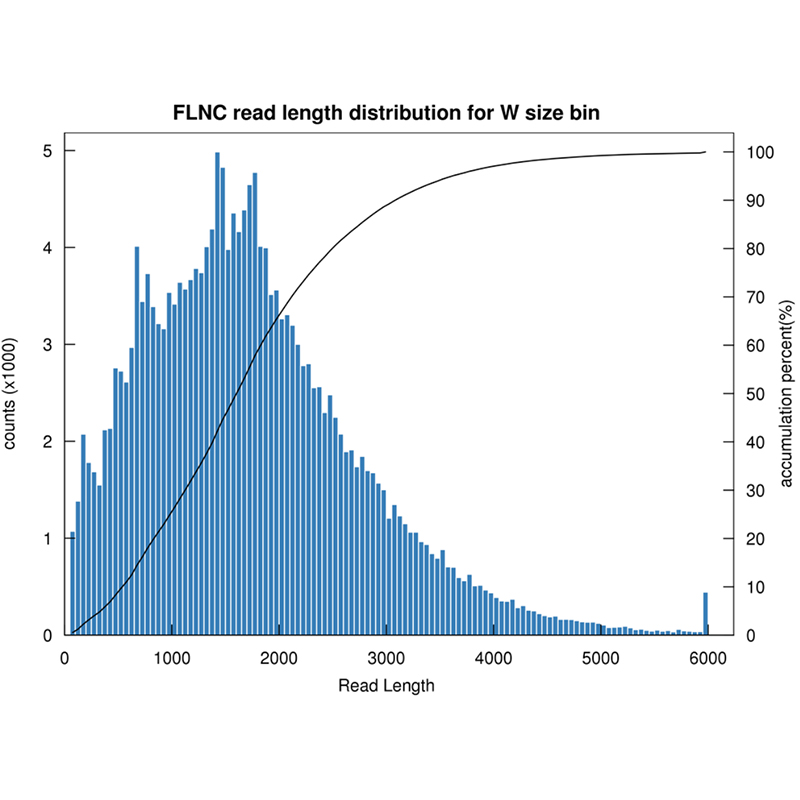
● Sequencing in CCS mode, generating HiFi reads
● Sequencing of the full-length transcripts
● The analysis does not necessitate a reference genome; however, it may be employed
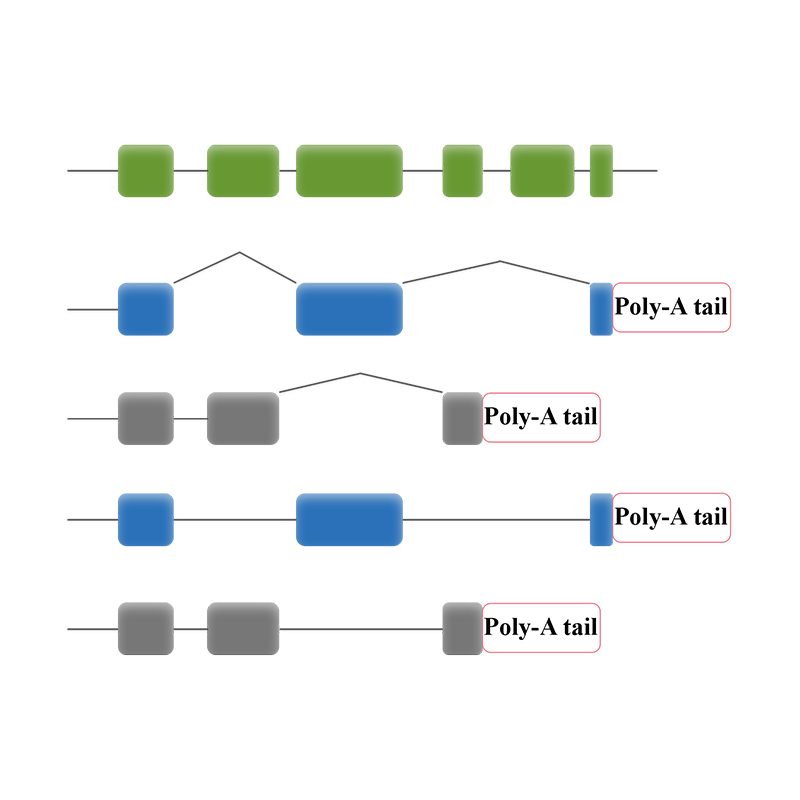
● Bioinformatic analysis enables analysis of transcripts isoform lncRNA, gene fusions, poly-adenylation, and gene structure
Service Advantages

● High Accuracy: HiFi reads with accuracy >99.9% (Q30), comparable to NGS
● Alternative Splicing Analysis: sequencing of the entire transcripts enables isoform identification and characterization
● Extensive Expertise: with a track record of completing over 450 PacBio full-length transcriptome projects and processing over 700 samples, our team brings a wealth of experience to every project.
● Post-Sales Support: our commitment extends beyond project completion with a 3-month after-sale service period. During this time, we offer project follow-up, troubleshooting assistance, and Q&A sessions to address any queries related to the results.
Sample Requirements and Delivery
|
Library |
Sequencing strategy |
Data recommended |
Quality Control |
|
PolyA enriched mRNA CCS library |
PacBio Sequel II |
20 Gb |
Q30≥85% |
Sample Requirements:
Nucleotides:
● Plants:
Root, Stem or Petal: 450 mg
Leaf or Seed: 300 mg
Fruit: 1.2 g
● Animal:
HEart or Intestine: 300 mg
Viscera or Brain: 240 mg
Muscle: 450 mg
Bones, Hair or Skin: 1g
● Arthropods:
Insects: 6g
Crustacea: 300 mg
● Whole blood: 1 tube
● Cells: 106 cells
|
Conc.(ng/μl) |
Amount (μg) |
Purity |
Integrity |
|
≥ 100 |
≥ 0.75 |
OD260/280=1.7-2.5 OD260/230=0.5-2.5 Limited or no protein or DNA contamination shown on gel. |
For plants: RIN≥7.5; For animals: RIN≥8.0; 5.0≥ 28S/18S≥1.0; limited or no baseline elevation |
Recommended Sample Delivery
Container: 2 ml centrifuge tube (Tin foil is not recommended)
Sample labeling: Group+replicate e.g. A1, A2, A3; B1, B2, B3.
Shipment:
1. Dry-ice: Samples need to be packed in bags and buried in dry-ice.
2. RNAstable tubes: RNA samples can be dried in RNA stabilization tube(e.g. RNAstable®) and shipped in room temperature.
Service Work Flow

Experiment design

Sample delivery

RNA extraction

Library construction

Sequencing

Data analysis

After-sale services
Includes the following analysis:
● Raw data quality control
● Alternative Polyadenylation Analysis (APA)
● Fusion transcript analysis
● Alternative Splicing Analysis
● Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs (BUSCO) analysis
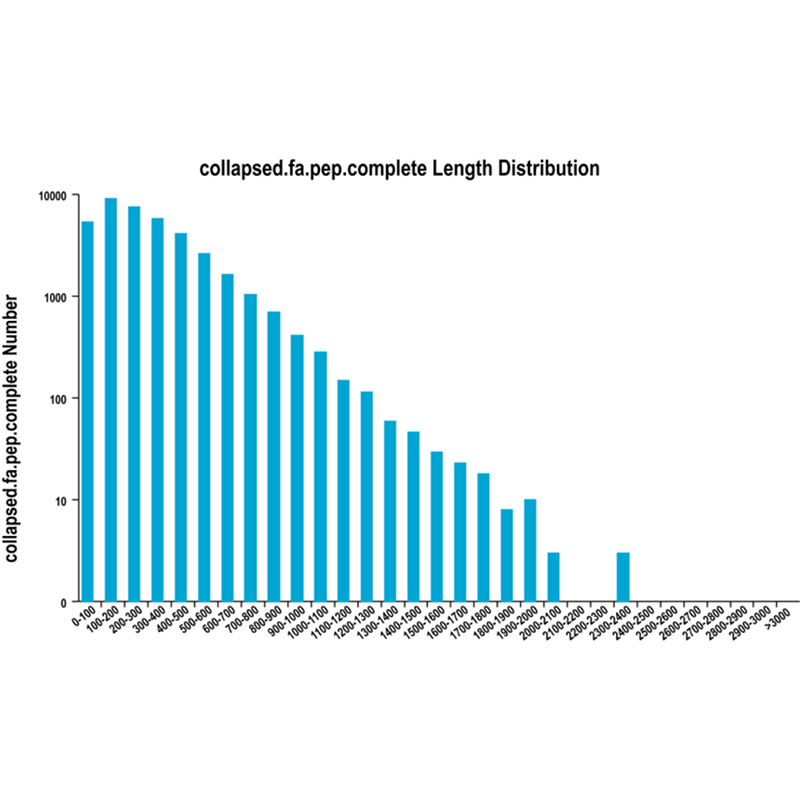
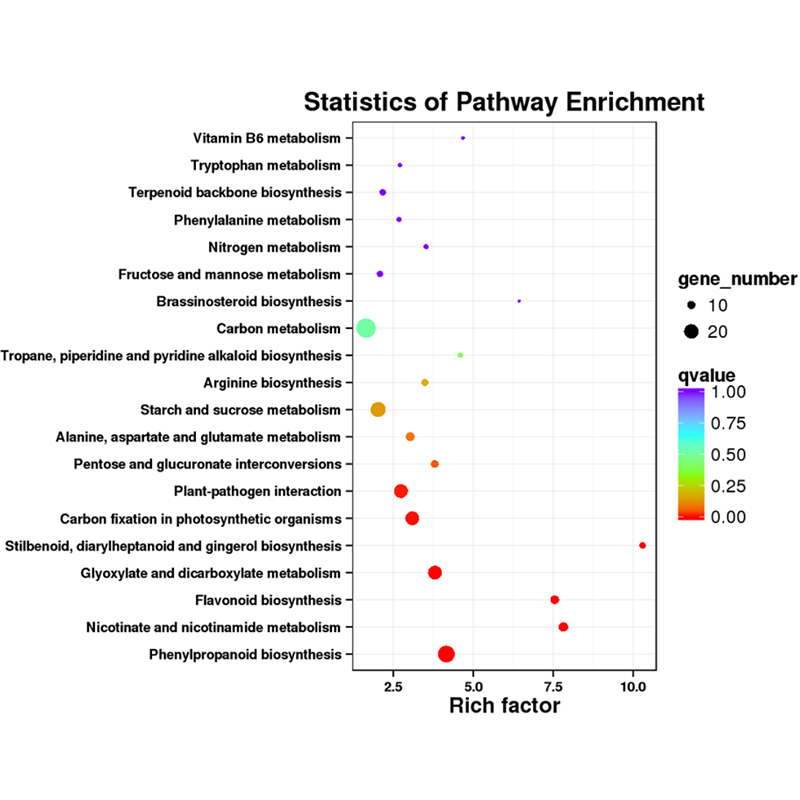
● Novel transcript analysis: prediction of coding sequences (CDS) and functional annotation
● lncRNA analysis: prediction of lncRNA and targets
● MicroSatelite Identification (SSR)
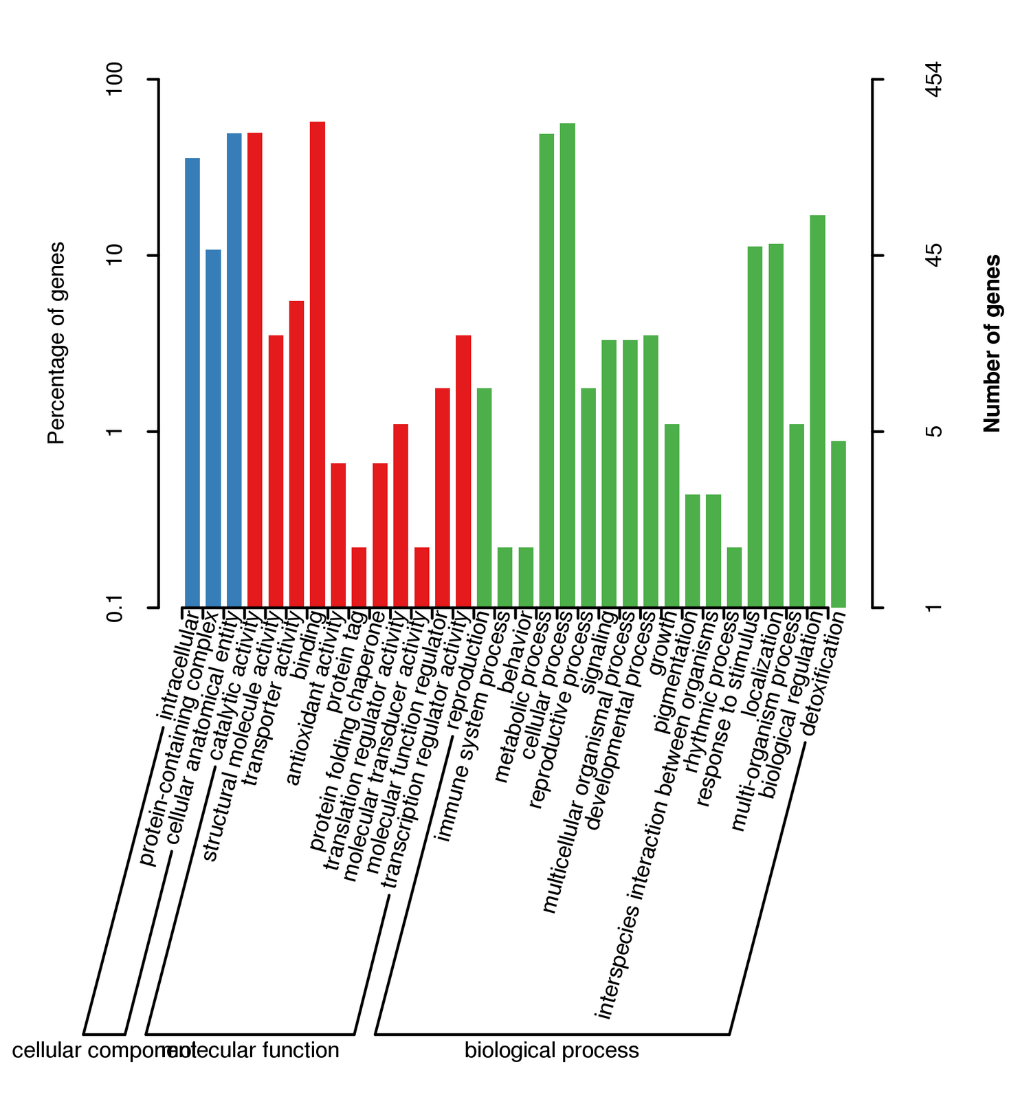
BUSCO analysis
Alternative Splicing Analysis
Alternative Polyadenylation Analysis (APA)
Functional annotation of novel transcripts
Explore the advancements facilitated by BMKGene’s Nanopore full-length mRNA sequencing services in this featured publication.
Ma, Y. et al. (2023) ‘Comparative analysis of PacBio and ONT RNA sequencing methods for Nemopilema Nomurai venom identification’, Genomics, 115(6), p. 110709. doi: 10.1016/J.YGENO.2023.110709.
Chao, Q. et al. (2019) ‘The developmental dynamics of the Populus stem transcriptome’, Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17(1), pp. 206–219. doi: 10.1111/PBI.12958.
Deng, H. et al. (2022) ‘Dynamic Changes in Ascorbic Acid Content during Fruit Development and Ripening of Actinidia latifolia (an Ascorbate-Rich Fruit Crop) and the Associated Molecular Mechanisms’, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), p. 5808. doi: 10.3390/IJMS23105808/S1.
Hua, X. et al. (2022) ‘Effective prediction of biosynthetic pathway genes involved in bioactive polyphyllins in Paris polyphylla’, Communications Biology 2022 5:1, 5(1), pp. 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03000-z.
Liu, M. et al. (2023) ‘Combined PacBio Iso-Seq and Illumina RNA-Seq Analysis of the Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) Transcriptome and Cytochrome P450 Genes’, Insects, 14(4), p. 363. doi: 10.3390/INSECTS14040363/S1.
Wang, Lijun et al. (2019) ‘A survey of transcriptome complexity using PacBio single-molecule real-time analysis combined with Illumina RNA sequencing for a better understanding of ricinoleic acid biosynthesis in Ricinus communis’, BMC Genomics, 20(1), pp. 1–17. doi: 10.1186/S12864-019-5832-9.